This article contributed by Liz Pekler(Bio).

Smartphone photography is the source of millions of images per day worldwide. It is not only an important aspect of social interaction, it is also a way to express yourself. Find out how to improve your shots and make the best of your smartphone photography.
Smartphone Photography is attracting more and more people. The number of images made on mobile devices exceeds the number taken on compact or DSLR cameras. Who could blame these keen users? Smartphones are easier to carry, cheaper to maintain, and are more user-friendly than the DSLR. And, with the constantly evolving smartphone camera apps and accessories, the future of smartphone photography seems assured. Indeed, smartphones and tablets are used in conventional photography too.
Is smartphone photography the new norm?
There’s no denying that DSLRs or mirrorless cameras are still the best types of cameras to have despite their larger size and weight. They have powerful sensors that offer the most megapixels. They allow complete user control over camera settings. However, more than that, they provide flexibility and freedom to use a range of accessories, like interchangeable lenses. The flexibility and control provided by a fully functioned DSLR can help you achieve the highest quality output.
Smartphone photography provides well for general image needs, like social media sharing and family records. Using mobile devices has become standard practice in recent years. Their hardware will need time to catch up on the quality and functions of more advanced cameras. However, there are many smartphone photography accessories available. These add-ons can enable your mobile device to get quite close to the high standard of DSLRs.
As long as smartphone manufacturers continue to develop higher specs and more powerful sensors smartphone photography will be likely to trend upward. However, no matter how good these mobile devices become, using the camera will require some user skill. The best photographs are not the product of the camera. They are a reflection of the vision and skill of the photographer – no matter what the device. Smartphone photography can be artistic, can be beautiful, can return great images.
You can get the best out of the built-in camera in your phones by practicing these helpful tips below:
Tips for Better Smartphone Photography
1. Pay Attention to the light levels
As with DSLRs, think, and make sure everything is good before touching the shutter button. Make sure the image is well-lit. One way to do so is to tap your subject on your phone’s display screen. In the smartphone camera on Auto mode, tapping on your subject will command the camera to focus on the area of the tap. Then the camera will make the exposure adjustment. That will ensure your subject is lit to its best advantage. The camera adjusts the overall image in proportion to the exposure. This shows the subject to its best advantage.
To manually adjust the scene’s brightness, swipe the ‘sun’ or ‘bulb icon’ after tapping on your subject. If you want to revert back to the default value, tapping anywhere on the screen of your smartphone usually does the trick.
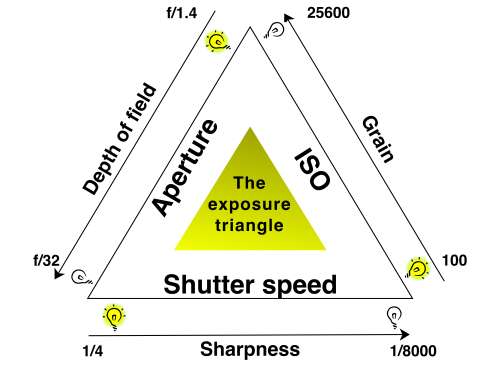
Brightness changes are not the best way to lighten your scene. You can over-whiten highlights – leading to distracting white burnouts. Instead, try manually adjusting your ISO levels. Higher ISO means the sensor is more sensitive to light. A high ISO number gives a brighter scene in proportion to the ambient light in the rest of the picture. This helps you adjust your image to avoid burnt out highlights.
Raising the ISO has a penalty. High sensitivity to light levels can make your photos look grainy. It is called digital noise. Dimly lit areas brightened by higher ISO are especially likely to show noise if you boost the ISO too high. Practice with ISO a bit to get a feel for the way to use it.
The best way to avoid digital noise is to add light sources or work with natural light. Camera sensors work well with good light levels. So, think about how you can enhance the light rather than rely on high ISO, if you can.
2. Apply the Principles of Composition
Another thing to significantly improve your smartphone photography is to compose your image. This means taking photos to create a more visually appealing image. Try not to “shoot from the hip”. The quick snap often leads to poor shots.
It helps to keep these basic rules of composition in mind when taking photos:
- The Rule of Thirds – Mentally divide the screen into a grid with 2 horizontal lines and 2 vertical lines. Then, align your subject with any of the guide lines or intersecting points to achieve a more natural-looking and attractive image.
- The Golden Ratio
 – When you compose your photo, leave 1.6 bits of empty space for every 1 bit of occupied space to achieve a balanced image.
– When you compose your photo, leave 1.6 bits of empty space for every 1 bit of occupied space to achieve a balanced image. - Leading Lines – Using lines in your composition will help influence viewing behavior, draw your audience’s eyes across an image or towards a subject, and adds motion and dynamism.
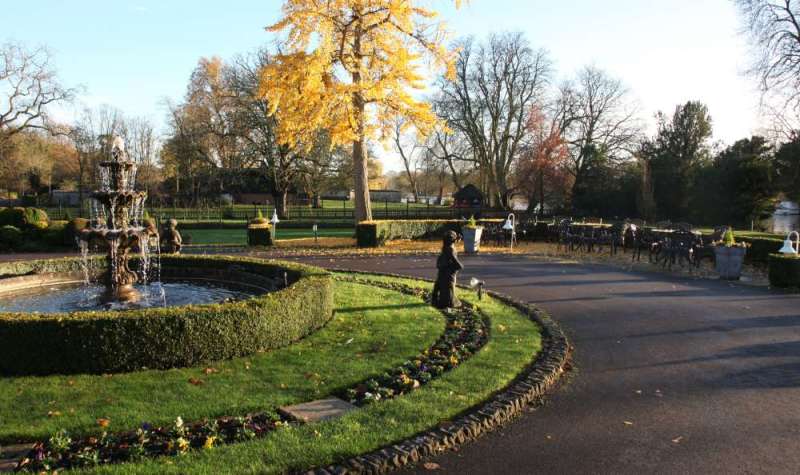
- Three-Layer Image – Having a foreground, a subject in the middle, and a background adds a sense of depth and interest to your photo. See “River Scene” below.
- Rule of odds – multiple subjects in an image are more attractive if they are an odd number. The most famous case is to have three of something, but five and seven are often used too.
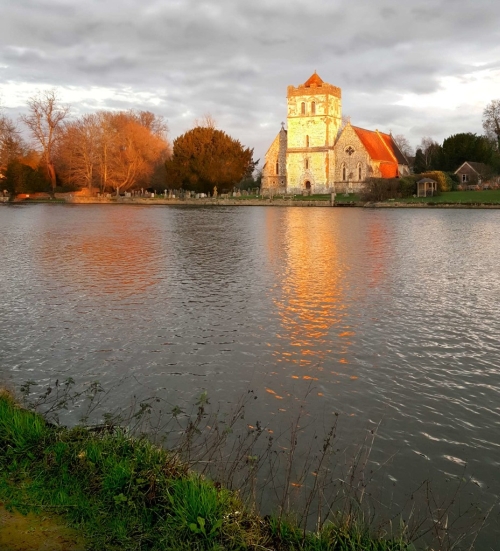

:: River Scene ::
This smartphone photograph shows three compositional layers. Introducing clear layers into your image helps to bring out a three dimensional depth and structure. Try to use foreground, mid-ground and distance layers in your images.
(Taken on a Galaxy S6 – Android phone)
(Click here to view large)
There are many ways you can use composition to improve your images. There is a whole page of composition links for you learn more here: Composition resources on Photokonnexion
3. Move as Close to your Subject as Possible
When using a smartphone to take photos, opt to move closer to your subject instead of using its zoom feature. Smartphone camera lenses usually have fixed focal lengths so they can’t zoom optically. Instead, it zooms digitally, which visibly distorts, pixelates, and lowers the quality of your images when overdone. Alternatively, you can use a compatible lens attachment that offers optical zoom capabilities.
4. Use Natural Light
The built-in flash on smartphones can sometimes be unflattering as it can wash out your subjects and produce harsh shadows. Harsh shadows with sharp lines create an angular appearance. This is particularly unflattering on faces.
To produce the best results, go for natural lighting. Natural light has an attractive quality for our eyes. We are naturally tuned to it. If you really need a flash there are some good attachments. You can use an attachable pocket spotlight or ring flash. Better still, use a more diffused light. An attractive diffused light provides just enough light for your subjects and creates flattering soft light with shadows. Shadows from soft light helps to create depth – giving a three dimensional feeling in the image.
5. Use A Third-Party Camera App
Your smartphone’s dedicated camera app can get the job done. However, third party apps allow you to do more with your phone’s built-in camera. Some of them offer better exposure adjustments, manual focus and camera settings (like shutter speed and aperture), or even integrated photo editing features so you can touch up captured photos instantly. If your interest is in better smartphone photography then use better editing too. Work to ensure you can navigate within the app and help you optimize its features for better photos.
Also familiarize yourself with the menu, settings, and features of your chosen camera app. If you’re a beginner, spend time and effort on learning photography basics. Think particularly about the shutter speed, ISO, and aperture. Also, think about how they relate to each other to create the exposure. Do some reading of this blog or other photography sites. Watch a YouTube tutorial on manual camera settings. Help yourself to develop a rounded approach to understanding both exposure and how best to take photos. Smartphone photography is as good for producing images as a DSLR. That is only true, providing, you know your tools and how to use them to produce a great image.
6. Take Advantage of the HDR Mode
The HDR mode on your camera phone allows it to take multiple shots of the same scene at different exposures, and then blend them together to create an image that pleases the eye. HDR mode blends the shots to create deeper contrasts in the image. This is particularly useful when shooting landscapes or high contrast scenes where there are obviously uneven highlights and dark areas. However, it must be used sparingly, as it can leave your images looking odd and overly edited. Don’t overuse it – try to work the editor so that your eye sees reality in the results. Trust your eye.
As a safety measure, also leave HDR on Auto. Then, you can manually pick out a better photo from the bunch of shots that were initially taken, in case the HDR blend goes badly. Apply the final result afterwards.
7. Post-Process Your Images
Post-processing can never replace good photography techniques. The best images stand alone for their beautiful content. However, it is also helpful to have editing skills. You can work to enhance a great image, or to work for the overall improvement of your photos. Take out spots, noise, or other irritations. Clean the image up so you show the beauty without distractions.
Photo editing apps like Instagram, VSCO, and Snapseed can be very helpful in making basic photo adjustments that will give you your desired result. Their photo filters are also great for setting or altering the mood of your images.
However, keep your edits at a minimum – especially processing ‘filters’. Instead, strive to make naturally beautiful images. This way, you don’t have to make too many adjustments later. After all, viewers can tell when you “cheat” your way to a good-looking image. Over-editing lowers the quality of your photos.
8. Keep Your Lens Clean and unscratched
This is something that is often overlooked by smartphone owners. It may not seem to be such a big deal for a small camera. However, a lens having oil, dirt, and moisture on it can slowly damage the glass. Leaving the lens on a tabletop can lead to scratching and marking. These ultimately affect image quality. Make sure you wipe the lens before use and use a protector or case, especially when doing a lot of outdoor shoots.
Can smartphone photography ever replace the DSLR?
Not all smartphones are capable of the more complex camera functions. However, many of the models some models currently on the market already have capabilities that mimic those found in DSLRs. In fact, many of them already allow control over the important camera settings, shutter speed, aperture, and ISO. These controls are native to some of the phones without having to use a third-party camera app.
Some of the latest smartphones, like the brand new iPhone and the latest Google Pixel, have more powerful and versatile cameras with more megapixels and other advanced features. Optical image stabilization for sharper photos and smoother videos is appearing, for example. The LG G6, released earlier this year, has great built in features. It carries a wide-angle lens that covers a larger area and is ideal for capturing group shots, magnificent architecture, and stunning landscapes. Many smartphone cameras from other brands offer other impressive features too. These advances are appearing just a few years after we thought such innovations wouldn’t be possible.
Smartphone photography is progressing fast. In a few years time, smartphone cameras are going to become even more sophisticated. For now, it’s safe to say that smartphones are definitely catching up, but whether they will ever surpass the DSLR remains to be seen. One thing is sure, the smartphone camera and DSLR are converging on each other. Furthermore, emergent technologies could take us anywhere. Camera technology still has a long way to go. Enjoy the ride!
Comments, additions, amendments or ideas on this article? Contact Us
or leave a comment at the bottom of the page…
Like this article? Don’t miss the next — sign up for tips by email.
Related articles/links:
Photokonnexion Photographic Glossary – Definitions and articles.
DSLR (A Glossary entry)
Using tablets in photography
Interchangeable lenses (A Glossary entry)
Shutter Button (A Glossary entry)
ISO (A Glossary entry)
Burnt out; highlights (A Glossary entry)
Digital noise (A Glossary entry)
Composition resources on Photokonnexion
The Rule of Thirds (Article)
The Golden Ratio ![]()
Compositional Lines
Rule of odds
Natural light (A Glossary entry)
Diffused light (A Glossary entry)
Soft light (A Glossary entry)
Shutter speed (A Glossary entry)
Aperture (A Glossary entry)
The Exposure Triangle
Optical image stabilization (A Glossary entry)
 Photokonnexion tips by email
Photokonnexion tips by emailIf you enjoyed this article please sign up for our
daily email service.
Find out more…