The choice is wide. Finding lenses requires careful thought.
Finding lenses that are right for you can be hard
Knowing what lens to buy is a challenge. It can be made simple if you have a few ideas. It is all about understanding your needs and making sure you fit the lens to a budget. First, some general advice about buying lenses.
Are you happy with the camera brand you own?
After a line of different cameras SLRs and different brands, my first digital camera was a Canon. It was my first Canon too. I was impressed. Well, they told me that Canon lenses were the best in the world! So I stayed with Canon.
I know, I know… you don’t agree with me on the best lenses. Whatever the outcome of that argument, I am not going there. That’s the whole point. Buying lenses is a personal decision. It relates to a range of needs and understandings you have about your photography.
You need to be completely happy with your camera brand before you buy lenses. Otherwise you will be stuck with a camera brand you don’t like and lots of money invested in lenses. Love the brand first. Then look for the ‘glass’.
Finding lenses… Things to consider
Usually the budget is fairly clear. However, I have one word of advice. Make sure you look at the upper range of your budget where the quality will be better. Don’t cut corners. Quality lenses don’t come cheap. There are lots of cheap lenses around, but you get what you pay for with lenses. They are expensive, but they are also high precision instruments. If the lens is cheap it probably will not be very robust and the quality of the optics will tend to be low.
After budget the next most important thing is to define your needs. It may be lovely to have a 500mm behemoth of a lens weighing two kilos and costing thousands. But if you are only in a position to use it once a year then it will not be worth investing. Far better to buy a more general purpose lens of higher quality to benefit your general photography and will use often. Focus on your regular photography action and expand your lenses around those activities. If you need that behemoth one weekend, hire or borrow one.
Defining your ‘needs’ is often confused with defining your ‘wishes’. Try to be realistic. Finding lenses is about knowing what you need. Only go for a lens that will be of regular, practical use. Do not define your needs based on your wish to pursue a dream. Most types of photography can be performed with a non-specialist set of lenses. Get good with those. Only buy good quality lenses to replace them. Only buy lenses when you can afford it. And, when you have the mega-once-in-a-lifetime trip actually planned, then factor in the specialist lens (if you really need it for most of the trip). Finding lenses suited to your needs is about being realistic about what you can achieve and how you will use them.
Of course the focal length and how ‘fast’ the lens is are both important. Also important is the type of lens – zoom, telephoto, prime, normal, wide angle and so on… However, most of these will come out in your decision around why you need the lens.
There are other things that are a little less obvious when finding lenses…
- Weight – Some people simply cannot hold up a big camera and a big lens. Be realistic about what you can handle.
- Size – especially for travel purposes, big lenses are a complication and a problem.
- Image stabilisation – Modern lenses usually have stabilisation – consider its weight, availability, cost and if you need it or not (large lenses are normally where there is an option).
- Glass quality – with professional grade lenses the glass is usually of very high optical quality. However, it is also expensive. So consider the importance of glass quality and overall lens quality for your budget and use.
- Brand name – Are you paying for a manufacturers reputation, or is the lens equalled by a third party manufacture – check the review websites. Ask around to see what other photographers think.
- Suitability for purpose – does the lens you want to buy actually suit your intended use. Check on the manufactures website, review sites or on discussion forums to get more information about the best type of lens for your use.
- Consider the insurance implications and cost. Covering several thousand pounds of lens for a foreign holiday is a significant extra cost.
Buying your lens
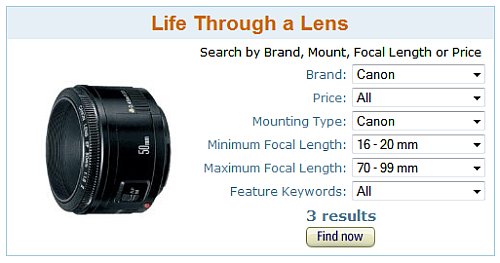
The sheer number of lenses available is bewildering. Finding lenses is best done with a finder tool. This tool for finding lenses on Amazon has made lens searches much easier.
The tool for finding lenses allows you to enter the factors that you consider important. It will return you a list of the available lenses to suit that purpose. After years of buying lenses I find this tool invaluable for helping to me to find a range of lenses from which to choose my ideal purchase.
If you want advice on what to do once your new lens arrives, check out this post: Getting started with a new lens.
 Photokonnexion tips by email
Photokonnexion tips by emailIf you enjoyed this article please sign up for our
daily email service.
Find out more…
Photokonnexion Photographic Glossary – Definitions and articles.
Also about ‘Finding lenses’: Buying lenses – a quick guide.
What is an SLR?
Definition: Focal Length
Definition: Fast Lens
Definition: Zoom Lens
Definition: Telephoto lens
Definition: Prime Lens
Definition: Normal Lens
Definition: Wide Angle Lens; Wide-angle lens; Wide angle

Damon Guy (Netkonnexion)
See also: Editors ‘Bio’.
By Damon Guy see his profile on Google+.