Look into your photograph, go deeper than it’s content.
Examine the composition of your image. Go beyond it’s immediate pictorial display. Look into the basic structure and you will be able to break your picture down into its component parts. Consequently, understanding individual “Visual Elements” in an image can help you to capture the eye of the viewer too. It’s these simple elements that make the eye work to absorb the content of an image.
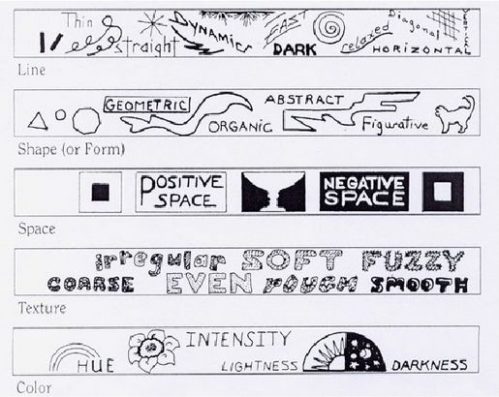
Image taken from the slide show below shows how the visual elements work.
What are the ‘Visual Elements’?
We make sense of the world by building a picture of it in our heads. Objects in our environment are visible to us because our eye/brain system is able to see and analyse the edges, contrasts, light/shadow/dark, colours and perspectives we see. Subsequently, our ability to analyse these patterns gives us an understanding of the world around us. So, if we can isolate these simple visual elements it will help our composition.
To make an image, photographers should look for strong visual elements through the lens. A great deal of the creative work in photography is to remove content that doesn’t contribute to the point of an image – these are distractions. So, to make the image effective we should also seek a point of view that isolates elements that we want to show.
Having isolated distractions the next job is to ‘see’ the subject in the ‘best possible light’. This English idiom is not just waffle (especially for photogs). It is really about using the edges, contrasts, light/shadow/dark, colours and perspectives mentioned above. Finding ways to use these effectively is what will draw the eye into our images. As a result, we should be finding simple, eye-catching features that make the scene realistic and easy to understand.
The Elements of Art
Research in art shows, that we can pin-point specific ‘visual elements’ in a photograph as powerful, but fundamental parts of our images. Artists have isolated these visual elements. They are called, “The Elements of Art”. There are seven of them…
- Line (The path of a point, or implied path of a point, through space or over a surface.)
- Shape (A two dimensional enclosure created by a single line – may be geometric or freeform.)
- Form (A three dimensional object which has a ‘mass’ or ‘weight’; a shape with depth; physical width/height/depth.)
- Space (Positive space: the subject or dominant object in the picture plane; Negative space: the background area. Space can occupy the outside, inside or surrounds in a depicted object.)
- Value (The relative brightness/lightness/darkness/colour intensity. Photographers usually refer to Value as ‘Tone’.)
- Colour (Light of particular wavelengths in the visible light spectrum.)
- Texture (The presence of an apparent surface that would have a touch/feel character of its own.)
Examples – a slide show!
Perhaps, some of my definitions above are difficult to understand. If you can put them into context it will help. Here is a short slide show by Kelly Parker. The examples really show the visual element of colour well. Click the bottom arrows to move back or forward on the slides. Furthermore, you can find examples of the other ‘Elements or Art’ available in many other articles. Search “Elements of Art“.
The Elements of Art – A glossary Entry
To follow up, the Photokonnexion Glossary has an extended article on the Elements of Art. You can see that here… Definition: Elements of Art
Download a Presentation Transcript of the slide show.

Damon Guy (Netkonnexion)
Damon is a writer-photog and editor of this site. He has run some major websites, a computing department and a digital image library. He started out as a trained teacher and now runs training for digital photographers.
See also:
Editors ‘Bio’.
See also:
Profile on Google+.

 Photokonnexion tips by email
Photokonnexion tips by email




