• Lag time – test one •
There is a gap between pushing the button and the making the photo.
(image by Netkonnexion)
Every time you push the button…
There’s a period when not much happens. Lag time is the total time taken for the camera to complete the exposure process from the button push. In that process is a lot of detail. Here we look at lag time. With a simple test you can get a feel for the lag time in your camera.
Why is lag time important?
If you buy a camera for action shots you want minimal lag time. Otherwise you look and press, but the action has gone. Of course you can anticipate the action. This is how we all deal with lag time. But to know what time to anticipate you need a feel for the camera. A long lag time is likely to make your guess about when to press the shutter button less accurate. So it’s in your interest to know the lag time and practice with it. If you know the lag it makes it easer to guess the delay for shots.
Shutter lag – don’t misuse the term
Some people use the term shutter lag in a confusing way. They mean it to be the same as lag time. In the past this may have been the case. In early cameras most of the exposure process was completed by the shutter. Today we have a lot of other steps involved. The list of various time related things in the exposure process is quite long today…
- LCD activation of the picture (LCD display and electronic [mirrorless] viewfinders only).
- Thinking time between seeing a subject on the display and the finger push on the button.
- Time taken to get a focus.
- Aperture – time to calculate & set aperture size.
- Meter – time from light reading to exposure set up.
- Digital sensor start up to be ready.
- Shutter motor/mechanism actuation.
- Shutter opening.
- Digital capture of light data.
- Shutter closing.
- Data emptied from sensor ready for next exposure.
These items may overlap, run simultaneously or be in sequence. Some may not apply to some cameras. It depends on the camera model, design, efficiency and the components involved.
This list adds up to the total lag time. The first five items are not shutter related. They delay the firing of the shutter. They are shutter delay times. The other items are shutter lag items. They are responsible for the shutter and sensor capture of the exposure. They determine the shutter process from start to finish. These are the shutter lag items.
To be clear, lag time is the sum of all the lag items. Shutter lag is only those items related to the shutter-sensor system.
For a more detailed look at various components of lag times check out: Definition: Shutter lag; Shutter delay; Lag time; Processing lag;
Getting the shot – lag time explored
In order to know your camera better you can actually measure your lag time. So here is a method you can use at home. I have tested it using two different pieces of equipment and on two cameras with good results.
A word of warning. The on-board flash crosses all the other lag/delay times and may extend your total lag quite a lot. This is because it takes time to charge up ready for the flash. It will affect the results. Before testing turn off your flash. Check your manual if you are not sure how. Both these methods have back-lighting. You will get enough light without it.
Explanation/method: to measure the lag time we need to identify all the processes involved. I have done this for you above. This allows you to know what parts of the process are holding things up. You will see later that can help you save time.
Next we need to find a way to mark the start and end of the process. Fortunately the camera helps us. When the shutter button is pushed we know the exposure process is started. The clever part is that if we photograph a timer we know when the exposure process is finished because the clock will show the finish time.
To find out our lag time is easy. We activate a clock at the same time as we push the shutter button. We do this while photographing the clock. When the shot is taken the end of the the lag time is shown on the photograph.
Two methods to try out
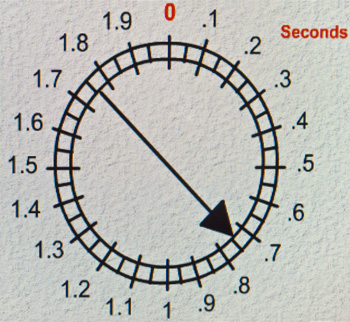
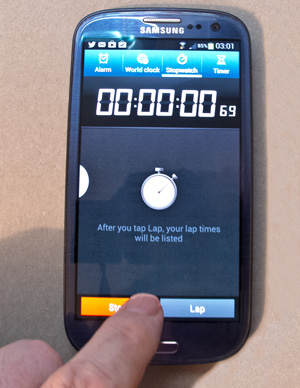
In the photo “Test one” above I have used this method with my smart phone. I set up the stop-watch app on my phone. Then I pushed “start” with my left hand. I simultaneously held the camera and pushed the shutter button. The key is to make sure you set off both the timer and shutter button at once. If you do, the the photograph will show the lag time. In the photo above it shows 69/100ths of a second. This is my lag time for a photo taken on my little Canon G12. Use a tripod or stand if holding your camera and pushing the button at once is not steady enough.
If you do not have a smart phone (or a stop watch) to photograph, try this web page…
This page will allow you to test your Digital Camera’s shutter lag…  .
.
(Note: this page is about your total lag time even though it refers to the shutter lag).
Follow the instructions on that page. You will see a very slight retard on the clock at the ‘zero’ point. That gives you time to notice the top point and press the shutter button. The resulting photo will tell you the lag time on your camera.
I have run tests on my camera using both the web page and the stop-watch app method. They give consistent results. I feel confident you will find either test will work for you.
Pre-focus to get the shot
Notice on the second test page there are two tests. The second one shows you how you can shorten your lag time. If you pre-focus the camera that saves some pre-shutter time. Focus takes quite a bit of time. So if it is already focused when you take the shot your lag is reduced.
To reduce the delay with pre-focus press the button half way down while looking at the clock. The camera will focus and take meter reading. Then you can hold the half way position – this is called focus-lock. Hold your half-down position until, at zero. Then push the shutter button the rest of the way down. You will normally find your camera lag time is greatly reduced. Possibly by as much as a half. Something to bear in mind for future shots.
Accuracy
Of course you might take a totally bad reading for your fist shot. After playing I found that for both methods you need to practice a little to get consistent readings.
To ensure you get a good overall result I suggest taking ten readings after some practice. Here are readings from my run of ten… 0.53 + 0.53 + 0.69 + 0.98 + 0.89 + 0.66 + 0.74 + 0.65 + 0.66 + 0.74 = 7.07
If we divide the total by ten we will get an average reading. It will iron out any anomalous readings.
Thus: 7.07÷10 = 0.71 (rounded to two places). The lag time on this camera is therefore 71/100ths of a second.
This ‘average’ method provides us with a consistent standard over our readings. This is a more accurate method of gauging the lag time.
What have we done?
The things a modern camera does to take a picture has created a long lag. The lag time is the sum of all the different things that impact the exposure process. From button-press to complete capture-of-data is the lag time.
We have looked at two ways of testing the lag time: a stop watch app; and a web page timer. I have also suggested using an average reading to iron out anomalies.
If you go through this process you will know your camera much better. But more to the point you will have a new confidence. You will know how long it takes to complete an exposure. And, you will know how much time to delay for a shot.
Comments, additions, amendments or ideas on this article? Contact Us
or why not leave a comment at the bottom of the page…
Like this article? Don’t miss the next — sign up for tips by email.

Damon Guy (Netkonnexion)
Damon is a writer-photographer and editor of this site. He has also run some major websites, a computing department and a digital image library. He started out as a trained teacher and now runs training for digital photogs.
See also:
Editors ‘Bio’.
By Damon Guy see his profile on Google+.

![]() . He has hit the nail on the head. The added context really makes the scene. Look for ways to add to the image. Make the scene your own by creating a new synthesis.
. He has hit the nail on the head. The added context really makes the scene. Look for ways to add to the image. Make the scene your own by creating a new synthesis.![]() has waited to capture the lady. She is not obscuring the art work. On the other hand the slightly odd pace gives it a new feeling. It is as if she is fleeing the scene. The whole picture, art work and lady, are something new. A synthesis of the original art work and the new aspect to the scene.
has waited to capture the lady. She is not obscuring the art work. On the other hand the slightly odd pace gives it a new feeling. It is as if she is fleeing the scene. The whole picture, art work and lady, are something new. A synthesis of the original art work and the new aspect to the scene.